 整体认识mybatis和mybatis的体系结构
整体认识mybatis和mybatis的体系结构
# 一、myBatis 核心概念
# 基本概念
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生类型、接口和 Java 的 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录
其它持久层解决方案对比:
JDBC、DataUtils、JdbcTemplate(搓衣板)、Hibernate(洗衣机)

mybatis3文档: mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介 (opens new window)
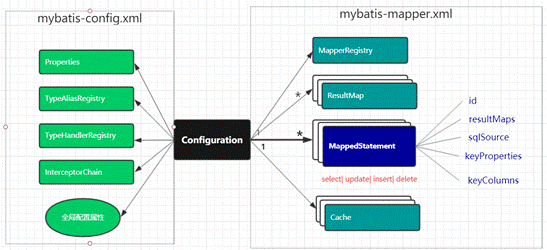
# 核心对象的作用域与生命周期
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.zxp.mybatis.dao.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUser" resultType="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.User">
select * from User where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ssm-demo"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/zxp/mybatis/dao/UserMapper.xml" ></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
Mybatis3.X 的版本使用的 dtd 作为 XML 的格式校验文档。 而在 XML 规范中,dtd 是有严格的顺序的:properties>settings>typeAliases>typeHandlers>objectFactory>objectWrapperFactory>plugins>environments>databaseIdProvider>mappers
运行
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper $proxy = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // 接口式编程
User user = $proxy.selectByid(1);
System.out.println(user.toString());
User result = session.selectOne("com.tuling.mybatis.dao.UserMapper.selectUser", 1);
System.out.println(result.toString());
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:
用于构建会话工厂,基于 config.xml environment 、props 构建会话工厂,构建完成后即可丢弃。
# SqlSessionFactory:
用于生成会话的工厂,作用于整个应用运行期间,一般不需要构造多个工厂对象, 建议弄成单例
# SqlSession:
作用于单次会话,如WEB一次请求期间,不能用作于某个对像属性,也不能在多个线程间共享,因为它是线程不安全的。
# 接口式编程
由于每次调用时都去找对应用 statement 以及拼装参数,使用上不是特别友好,myBatis 引入了接口的机制,将接口与mapper.xml 的namespace 名称绑定,MyBatis就可以根据ASM工具动态构建该接口的实例。其原理是通过动态代理来实现。
mapper 映射器接口实例: 通过 session.getMapper(Class
# 二、全局的 configuration 配置
mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 配置 (opens new window)
# 1、properties属性
properties 元素可以通过 resource 或url 加载外部 properties文件中的属性,也可以直接设置property 属性。然后在xml 中就可以通过${属性名}进行引用替换。
<properties resource="app.properties" url="">
<property name="jdbc.driver" value="com.oracle.jdbc.Driver"/>
</properties>
2
3
resource= app.properties 从class path中加载
url=[file:///G:/git/tuling-mybatis/src/main/resources/app.properties](file:///G:/git/tuling-mybatis/src/main/resources/app.properties) 基于url加载
引用属性方式:${jdbc.user}
从 MyBatis 3.4.2 开始,位符指定一个默认值。例如:${jdbc.user:root}
# 2、环境配置
一个项目经常需要在例如开发坏境、测试环境、预演环境、生产环境中等不同环境中进行部署,每个环境所对应的参数是不一样的,myBatis 中可以通过 environment 来设置不同环境的属性。
<environments default="${default.environment}">
<environment id="test">
<!--type=JDBC|MANAGED-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- type=UNPOOLED|POOLED|JNDI-->
<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="dev">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
可通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build( environment) 来指定初始化哪套环境。
# 3、设置
设置MyBatis 全局参数,约定myBatis 的全局行为
<settings>
<!-- 开启二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 开启驼峰命名适配-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 插入时,设置id -->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true" />
<settings>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
示例驼峰命名开启与关闭:
- 尝试开关 mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 属性 来观察Account 数据查询情况。
# 4、别名
在myBatis 中经常会用到 java 中类型,如sql 块中中 parameterType 参数引用中 javaType 结果集映射的javaType ,都要使用java 全路径名,可以通过
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.Account" alias="account"/>
<package name="com.tuling.mybatis.dao" />
</typeAliases>
2
3
4
提示:建议不要设置。因为常用的类 mybatis 已经内置别名,而自定义的类设置别反而不好去找,影响阅读。
# 5、类型处理器
持久层框架其中比较重要的工作就是处理数据的映射转换,把java 类型转换成jdbc 类型的参数,又需要把jdbc 类型的结果集转换成java 类型。在mybatis 中是通过 TypeHandler 接口来实现的。
可以看到 typeHandler 就是两个作用 设置参数 与获取结果。
你可以设置自定义处理器
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.mybatis.example.ExampleTypeHandler" />
</typeHandlers>
2
3
可以通过以下两种方式指定处理的范围
javaType="long", jdbcType="Date"
@MappedJdbcTypes( jdbc类型) @MappedTypes java类型
示例:
long 类型时间戳转换成 日期类型
添加算定义处理类:
public class LongTimeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Long> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Long parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setDate(i, new Date(parameter));
}
@Override
public Long getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
return rs.getDate(columnName).getTime();
}
@Override
public Long getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return rs.getDate(columnIndex).getTime();
}
@Override
public Long getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return cs.getDate(columnIndex).getTime();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
在resultMap中指定 typeHandler:
<resultMap id="account2" type="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.Account">
<result property="createTimestamp" column="createTimestamp"
typeHandler="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.LongTimeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectById2" resultMap="account2">
select a.*,a.createTime as createTimestamp from account a where id = #{id}
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
也可以在mybatis-config.xml里面指定, 上面可以不用注解了
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="com.zxp.mybatis.handler.LongtimeTypeHandler" javaType="long" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" />
</typeHandlers>
2
3
# 6、mappers映谢器
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/> // classPath目录下
<mapper url="http://www.xxx.com/xml/BlogMapper.xml"/> //url方式加载, http ftp file:
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/> // 类跟xml得在一个目录下
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
2
3
4
5
6
加载方式:
resource 基于classPath 加载xml文件
url:基于资源定位加载xml 文件
class:基于接口加载
package :扫描包下所有class 然后进行加载
约定规则:
mapper 中的 namespace必须与对应的接口名称对应。
通过 class 或package 中加载时 .xml 文件必须与接口在同一级目录。
# 三、mapper 文件

mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器 (opens new window)
# sql语句块statement
通过原生JDBC写DAO的年代 ,程序员最怕莫过于拼接SQL语句,拼接参数与设置返回结果集,Hibernate 将拼接SQL时代成为过去,通过ORM映谢,完全不需要处理任何SQL,但这又带来了新的问题就是。无法编写自定义SQL从而丧失了灵活活及更好的性能。MyBatis 通过 mapper 映射SQL很好解决了这一点。它无需在JAVA代码中拼接SQL,而是将其移至mapper 文件集中处理SQL节约了大量的开发时间。
# Mapper中的元素
cache – 对给定命名空间的缓存配置。
resultMap – 结果集映射。
sql – 可被其他语句引用的可重用语句块。
insert – 插入语句
update – 更新语句
delete –删除语句
select – 查询语句
# select 用法及属性
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.Account">
select * from account where id = #{id}
</select>
2
3
属性:
<select
id="selectById" <!-- 语句块的唯一标识 与接口中方法名称对应 -->
parameterType="User" <!--参数java类型-->
resultType="hashmap" <!--返回结果java类型-->
resultMap="userResultMap" <!--返回结果映射-->
flushCache="false" <!--true 每次调用都会刷新 一二级缓存-->
useCache="true" <!--true 是否保存至二级缓存当中去-->
timeout="10"
statementType= PREPARED">
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# insert&update&delete 用法
<insert
id="addUser" <!-- 语句块的唯一标识 与接口中方法名称对应 -->
parameterType="User" <!--参数java类型-->
flushCache="true" <!--true 每次调用都会刷新 一二级缓存-->
statementType="PREPARED" <执行类型>
keyProperty="" <!--主键对应的java 属性,多个用 逗号分割-->
keyColumn="" <!--主键列,多个用 逗号分割-->
useGeneratedKeys="true" <!--插入成功后将 将值回设至 原参数->
timeout="20">
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
示例:
<insert id="addUser" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true"
parameterType="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.User">
insert into user (name,updateTime,createTime) values (#{name},#{updateTime},#{createTime})
</insert>
2
3
4
# 参数映射
参数映射是最强大功能之一,基可以通过以下方式进行引用
- 单个简单参数引用 :如果方法中只有一个参数可通过任意名称 进行引用
-多个简单参数引用:通过参数下标引用 #{arg0} #{arg1} 或 #{param1} ,#{param2}
对像属性引用: 直接通过对象属性名称引用,嵌套对像通过. 号进行引用
map key值引用:
变量名称引用(需要jdk1.8支持) :通过方法中参数名称引用,需要jdk1.8支持,且在编译时必须加上
-parameters编译命令
# 在idea 中添加 编译参数

# 在maven中添加编译参数
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
注:一旦通过变量名称引入不在支持arg0获取! 因为编译后的变量名不再是arg1, 其通过反射可以拿到变量名
# 参数引用相关属性
javaType=int, #参数java类型
jdbcType=NUMERIC,# jdbc类型
typeHandler=MyTypeHandler# 指定类型处理器
参数拼接${}
基于#的参数引用 其原理是通过 ?占位其通过预处理能获得更好的性能 和安全性(防止SQL注入)但有些需求是通过?占位无法实现的,比如在一些分库分表的场景中我们需要 动态的拼接表结构。比如某系统日志表是按年进行切割的 2018_systemlog,2019_systemlog这时就可以通过
示例:
@Select("SELECT * FROM ${table} WHERE id = #{id}")
User selectByTable(String table, int id);
# 结果集映射
结果集映射是指 将resultSet 中内容封装转换成java对像,在纯jdbc时代全部都是用调用resultSet的getXXX(columnName) 来获取属性并封装。代码量大,编程效率低尤其当数据模型是1对多,或多对多这种复杂关系,这种封装代码将会变得非常复杂。结果集映射就是为解决这个问题 通过resultMap 集中处理结果集与JAVA对像的关系。
结果集自动映射
在select 中指定 resultType="" 后无需要任何配置 myBatis 会基于 resultType中的JAVa类型及属性自动推断生成 一个隐示的resultMap 从而完成结果映谢
resultMap
但有时jdbc 并不是与java Bean 完全贴合这时就需要手动设置resultMap
<resultMap id="account2" type="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.Account">
<id property="id"/>
<result property="createTimestamp" column="createTimestamp" typeHandler="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.LongTimeHandler"/>
</resultMap>
2
3
4
这时在select元素中用 resultMap ="account2" 即可引用该map映射。
基本元素与属性
ID:用于结果集中的唯一标识, 缓存就以它作为标识
result:设置一个某通过字段
- property: 类的属性
- jdbcType: 一般不需要指定,如果有空,就要指定, 见枚举
JdbcType
- jdbcType: 一般不需要指定,如果有空,就要指定, 见枚举
- javaType: 类的类型: long, int等
- column: 数据库的列
- typeHandler: 指定转成java类的类型转换器, 不指定的话,可以根据jdbcType和javaType自动找到对应的typeHandler
# 嵌套结果映射
关联 association ,如下只有一次查询
<resultMap id="accountAndUser" type="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.Account">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<association property="user" javaType="com.tuling.mybatis.dao.User">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="name" column="userName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAccountAndUser" resultMap="accountAndUser">
SELECT a.*, b.name userName from account a,user b where a.user_id=b.id
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
引入外部Select, 会有两次查询
<!--基于多次查询拼装引入 -->
<resultMap id="accountAndUser2" type="com.zxp.mybatis.bean.Account">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" />
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" />
<result property="money" column="money" />
<result property="userId" column="user_id" />
<!-- 根据type类型会自动找到LongtimeTypeHandler,也可以指定typeHandler -->
<result property="updateLongTime" column="update_time" javaType="long" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
<association property="user" javaType="com.zxp.mybatis.bean.User" column="user_id" select="getUser">
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUser" resultType="com.zxp.mybatis.bean.User" >
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
集合collection
mybatis官方文档:http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
